Newborn Bunnies: Rabbit and Rabbit Care
Breeding rabbits requires some knowledge from the owner of the animals, in particular, about caring for the female and the cubs during the round-up. This article discusses the possible difficulties in growing young animals and their solution.
Okrol
Pregnancy in rabbits lasts an average of 30 days. The female in this period is called the sucral, and the moment of resolution from the burden is called okrol. When the female begins to fuss, pull out her own fluff - this means that okrol is nearing. The owner is required to build a queen cell: a wooden box, the bottom of which is covered with soft straw. For thermal insulation, the female additionally covered the nest with down.

Ordinary domestic rabbits are kept and breed when kept outdoors in cages, ornamental individuals - at home. Childbirth usually occurs at night, within 10 minutes - hours. As a result, on average, up to 9 babies are born. After the birth of all litter, a baby place leaves, which the female eats, replenishing the supply of useful elements. After laying the offspring in a nest, she proceeds to lick and feed them.
Did you know? The rabbit may have a false pregnancy, in which she behaves in the same way as a fertilized individual. False pregnancy lasts about two weeks.
The appearance of rabbits
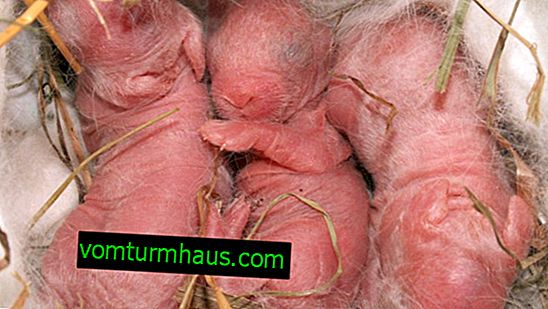
Cubs are born completely helpless: naked and blind. The weight of newborns is from 40 to 80 g, but after a week the weight doubles.
Rabbits are developing rapidly:
- 3 days - fluff appears;
- 7 days - hearing develops;
- 17 days - the change of teeth begins;
- 27-30 days - completely covered with wool;
- 45 days - weight up to 1.5 kg.

When they open their eyes
Rabbits, like many mammals, are born blind. With normal care of the cub from the first days of life on the 10th day, the palpebral fissure begins to erupt. If teething is delayed for more than two weeks, you need to check the purity of the eyes. Perhaps pus has accumulated on the baby's eyelids. The accumulations are removed with a cotton swab dipped in saline.
First lure
At the age of two weeks, offspring begin to feed:
- soft hay;
- grated carrots;
- herbal granules and fresh herbs;
- mashed potatoes;
- oatmeal.
Over the course of a week, they are gradually accustomed to coarser feeds: compound feed and mash mats.

Exit from the nest and inspection of young animals
Youngsters begin to be interested in the surrounding world after their eyes are completely open. The rabbits begin to leave the nest for a brief period in order to examine their surroundings. For a long time, pets spend outside the nest at the age of 17–20 days. Find out more after how many days the rabbits get out of the nest. During this period, a detailed examination of the young is carried out:
- determine the sex of the cub;
- weighed;
- look at the condition of the coat;
- examine the ears, eyes, nose;
- check the condition of the abdomen and anal area.
The first inspection of the offspring is carried out after childbirth, they are considered living individuals, they are removed from the cell of stillborn.

Female weaning process
The moment of deposition from the female is determined by the owner of the animals, depending on the breed and the desire for the next rabbit cover.
Baby weaning age:
- early - 30 days;
- average - 40–45 days;
- late - 60 days.
Behavior and condition of young animals during this period should be observed. New feed is introduced gradually.

Refusal of rabbits to feed cubs
It happens that the female refuses to feed the cubs. This happens for a number of reasons that the rabbit breeder needs to study in order to rectify the situation.
Causes
Refusal of feeding is not necessarily caused by an undeveloped maternal instinct. Did you know? In rabbits, a double uterus, they can bear two offspring at the same time, and conceived in different periods. Common causes in this situation and solution to the problem:
- The age of the female is the first large litter of a young dairy female who is physically unable to feed a large number of cubs. For example, the number of individuals in the offspring is 12, and the mother’s nipples are only 8. In this case, some of the rabbits are planted in the experimental uterus.
- External factors - noise near the cells or the presence of pungent odors, too bright lighting can provoke stress in the female, which will affect lactation. The mothers are satisfied in a quiet place, excluding the close proximity of other animals, mechanisms and sharply smelling household chemicals. It is also advisable to exclude the proximity to the mother liquor of a mature male; its smell can confuse the rabbit.
- Postpartum hunting - some individuals are ready to mate several days after giving birth, in this case the female will not only refuse to feed the offspring, but can also be dangerous for the cubs. For this period, rabbits are best planted to another female.
- Inflammation of the mammary glands - the rabbit will refuse to feed the babies due to pain. The diagnosis must be confirmed by a veterinarian. After appropriate treatment, the behavior of the rabbit will return to normal. Mastitis can be caused by cold, so a pregnant and lactating female must be kept warm, on a thick litter.

Artificial Feeding
Complete weaning from breast milk significantly reduces the immunity of rabbits and the percentage of survival of young animals, so several factors must be taken into account:
- choosing the right mixture;
- meal schedule;
- dosage
- hygiene rules;
- care for the artificers.
- whole goat milk;
- milk powder for cubs of animals (in a pet store);
- condensed milk diluted with boiled water 1: 1.
- from the 1st day to a weekly age - 5 times a day;
- from the 8th day - 2-3 times a day.
- 1-7 days - 5 ml;
- 8-14 days - 10 mg;
- 15-20 days - 20 mg.
We recommend that you learn more about artificial feeding of rabbits without a rabbit. Feeding rules and care procedures:
- First, the cub’s oral cavity is lubricated with a milk mixture so that it licks it.
- For feeding use a syringe and a pipette, gradually accustoming to a bottle with a pacifier. Get "dishes" in a pet store or veterinary pharmacy.
- All feeding devices must be sterile. Farmer personal hygiene is also required.
- Before each feeding, a procedure is performed to empty the intestines and bladder, imitating the actions of the mother. With a wet towel, massage the stomach from the navel to the hind limbs.
- The rabbit is fed gently, wetting the oral cavity so that the mixture does not enter the respiratory system.
- The cub is held upright in the hand, trying not to squeeze much.
- The mixture should be freshly prepared and warm - + 37 ° C.
- Newborns should not receive more than 1 ml per feed, otherwise there may be an upset stomach.
- After feeding the cubs' faces, they must be thoroughly cleaned with a wet towel to remove food debris.
- Keep the kids warm, the optimum temperature is + 25 ... + 28 ° C.

Sharing to another female
Replanting to another female should take into account several nuances.
Rules for successful replanting:
- The optimal difference in the age of offspring (their own and planted) is 2-3 days.
- You need to choose an adoptive mother from experienced, already raised foreign babies of females.
- At the time of the "lining" the rabbit is removed from the mother liquor.
- Farmer's hands should have a neutral smell.
- Before placing the rabbits in a strange nest, they are rubbed down from this mother liquor to deceive the female.
- The adoptive mother is returned after 1-1.5 hours.
Forced feeding
Inexperienced females experience genetic malfunctions when the rabbit simply does not know how to take care of the offspring. In this case, forced attachment to the mother's breast can normalize the situation.
Procedure:
- To carry out the manipulations, an assistant will be needed that will hold the female while the farmer applies the cubs to her nipples.
- Clothes and hands of both “breadwinners” should not have extraneous odors.
- Rabbits are removed from the nest and placed in a box, wrapped in a clean rag.
- The female is immobilized, laying on her side, holding her fore and hind limbs.
- Rabbits are applied to the nipples in turn at intervals of approximately 15 minutes. This time is enough to saturate the cub.
- The fed babies are put in another box so as not to confuse well-fed and hungry individuals.
- After the procedure, the rabbits and the female are returned to the mother.

Problems with growing rabbits
When breeding rabbits, each farmer may encounter a number of problems. Difficulties can arise both during pregnancy and after a nursing round, and after it.
Premature birth
Premature okrol, which does not cause fear and is not dangerous for babies, happens on the 28th day of pregnancy.
Reasons for early birth:
- the age of the female is 2-3 years or more;
- multiple pregnancy;
- okroli following after a short period of time;
- too low or high temperature during the gestation period.

Factors causing pregnancy fading:
- poor nutrition; poor diet;
- female diseases, in particular of an infectious nature;
- nervous stress.
To avoid this, a pregnant female is provided with attentive care:
- a balanced diet;
- keep warm and clean;
- always available fresh water;
- scheduled veterinary examinations.

Mortality of newborns
The death of an offspring after a couple of hours, a day or the birth of dead cubs most often occurs due to infection of a pregnant rabbit with an infectious disease, so it is important for the farmer to know what the rabbits are sick with and to vaccinate them in time.
The following diseases of pets lead to sad consequences:
- hemorrhagic disease (HBVC);
- coccidiosis;
- listeriosis;
- myxomatosis;
- pasteurellosis;
- tularemia;
- fascioliasis.
Non-viable cubs often appear due to errors in the care of the female:
- stress;
- poor nutrition;
- non-compliance with the regime of detention.

Female scatters cubs
The behavior of the females after the birthing, their attitude to the cubs also depends on the conditions of detention and health status. Find out more about why the rabbit spreads the rabbits right after the bunny. Factors due to which the female scatters rabbits:
- psychological state - a problem can arise as a result of stress: due to the proximity of other animals, smells, noises. Eliminate the causes of a nervous breakdown - and the behavior of the rabbit will improve. Aggressive animals that trample their offspring for no apparent reason should be discarded;
- a sick animal is best not allowed to mate at all . The rabbit, weak after childbirth, will not be able to look after the offspring, she will scatter him;
- mastitis - most often infections of the mammary glands develop due to bites of cubs and poor hygiene in the cell;
- in addition to hygiene, it is important to properly equip the mother liquor - it should be roomy, warm and not fall under bright lighting;
- improper diet of the female - a hungry mother will discard cubs from herself, because she has poor lactation due to malnutrition;
- hunting - for a female who is ready to mate immediately after a boiling, it is advisable to carry out a “soothing” mating, after which she can return to her duties.
Female cannibalism
The absence of maternal instinct and possible postpartum problems can be predicted by the behavior of the pregnant woman. She will not show the slightest desire to equip the nest. We advise you to read what to do if the rabbit eats rabbits. Other reasons for eating offspring:
- after a bunny rabbit feels an acute shortage of nutrients in the body and intense thirst. If the owner of the animal does not worry about enough water in the cage, about a balanced diet, the female can eat newborns;
- lack of milk will force the rabbit to eat the weakest cubs to feed the remaining viable;
- cannibalism can cause severe stress. After the rounding, the rabbit needs peace and silence, feeling safe for posterity;
- the close presence of the male and the urge to "hunt".

Rabbits squeak
The main reason that the cubs crawl out of the queen cell and squeak is hunger. The first thing to do is to examine the cubs. If they have hollow bellies, their skin wrinkled, which means that the mother does not have enough milk. It is necessary to review and adjust her diet.
It is also advisable to make sure that the mother liquor is warm enough. Cold can push kids to look for a warmer place. Perhaps a heater needs to be installed in the cage. Important! A cage with offspring must be carefully inspected and protected from predatory rodents (rats, weasels). Often the young are eaten by predators, and not the rabbit mother. The success of rearing young animals depends largely on the farmer. He must create the most comfortable conditions for the puppy rabbit, think over a balanced diet and equip the mother-bird.












