How to treat fusarium wilting pepper?
Sweet pepper belongs to the Solanaceae family and develops diseases characteristic of this group of vegetable crops, in particular, Fusarium wilting is common. What is this ailment, and how to deal with it - read the article.
What is it and what is dangerous?
The causative agent of fusarium wilting (also fusarium) of pepper is a fungus of the genus Fusarium, which is common in all climatic zones. Not only solanaceous plants can infect, but also other vegetable and fruit crops, cereals and flowers. Therefore, it is important to detect the disease at the beginning of development in order to prevent the spread. Fusarium penetrates through the roots of pepper, since it can be stored in the soil for a long time, and develops in the vessels of the stems, after which the mycelium clogs them and begins to poison with toxins.
Important! With proper watering, there is a chance that the vegetable will still have time to bear fruit.
Thus, the process of nutrition of the plant organism malfunctions. Plants can be infected, regardless of age, at any stage of development. The sapling will begin to wither a few days after it was infected. The leaves curl and turn yellow, as a result, the vegetable crop begins to wither and die 10–20 days after the first signs appear.

Causes and signs of damage
Sources of infectious onset are:
- plant residues and soil containing fusarium;
- mechanical clogging of seeds can sometimes be noted;
- high temperature of air and soil is favorable for the development of fusarium (+25 ... + 28 ° С);
- acidic or heavy soil;
- agricultural equipment;
- finding a personal plot close to highways and industrial zones;
- insufficient soil moisture;
- uncontrolled use of fertilizers and chemicals.
Important! The disease can remain in the soil and on plant debris for 10 years or more.
Signs of a vegetable lesion:
- at the very beginning you can notice only a slight wilting and yellowing of the upper foliage;
- after foliage, it begins to change color from pale green to yellow brown;
- the surface of the infected peppers located at the stalk is covered with pressed, dried areas of dark color;
- in case of increased humidity, sporulation of a pinkish color on the surface of necrosis may develop.

How to deal with pepper fusarium?
Unfortunately, if the plant has undergone a disease, it cannot be cured. In the early stages, the problem is difficult to detect, since it usually starts with the roots, so the plant affected by the disease will have to be removed and burned. And remove along with an earthen lump. And the place where the plant was, pour copper sulfate. But the disease can be prevented by observing preventive measures, as well as performing agricultural techniques, processing with chemicals and folk remedies.
Find out why bell pepper wilts and shrinks.
Chemicals
Today there are drugs that inhibit the development of the fungus or destroy it. You can use not only chemical, but also bacterial preparations against fusarium wilt. Fusarium is caused by a fungus, so if you populate the soil with antagonistic bacteria, they will displace the disease.
The following chemicals are used to combat pepper fusariosis:
- "Maxim" - process the material for planting;
- “Vitaros” - gives color to the processed material for planting and retains the effect for a long time;

- "Fundazole" and "Topsin-M" are systemic fungicides that process seeds and water plants.

But it is better to use biological preparations that do not have a harmful effect, for example:
- Agat-25K . In addition to the negative effect on the source of fusarium, the drug also positively affects the growth and yield of pepper;
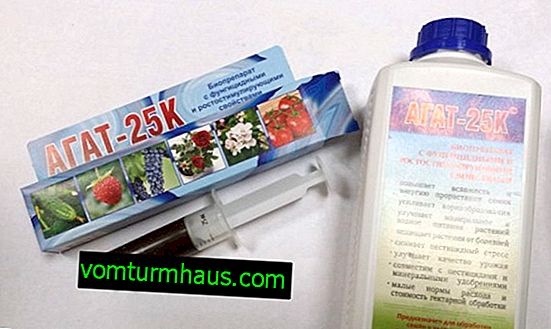
- "Bactofit" - promotes healthy microflora and displaces pathogenic fungi;

- "Gliocladin" ("Trichodermin") is used to prevent fusarium wilt, and also improves soil properties;

- potassium humate - has a fungicidal effect, seeds are treated with it, introduced into the ground, pepper is also treated specifically;
- Fitosporin-M . It is a microbiological tool for processing soil and planting material before planting or storage.

Folk remedies
The causative agents of the disease do not live in soil saturated with calcium and having a neutral pH level. Therefore, dolomite flour or chalk can be added to acidic soil. If the pH is less than 4.5, dolomite flour is added to 500-600 g / m², 350-400 g / m² is sufficient in less acidic soils (pH from 5.2 to 5.6). Chalk should be used 2 times less.
Did you know? One large fruit of pepper contains the daily intake of vitamin P for an adult. Regular consumption of vegetables reduces the permeability and fragility of capillary vessels.
For prevention, soil and non-infected plants are treated with the following means:
- Per liter of milk - 25 g of grated laundry soap . Stir thoroughly and add 35 drops of iodine. Plants are treated with this solution.
- Infusion of marigolds (black-browed) . Half a bucket of dried marigolds is poured with 10 liters of water and insisted for 2 days. Spray the plants.
- A glass of wood ash is mixed with 1 tablespoon of laundry soap and mixed in 2 liters of water . Insist 2 days. After that, the bushes and the soil are treated. After a week, repeat the procedure.
- 3 kg of wood ash are poured into a bucket of hot water . Insist 2 days and water the soil around the plants.
- The head of garlic is crushed and insisted 1 day in a liter of water. Filter and add another 9 liters of water and immediately spray the plants.
- Onion husk (about 2 handfuls) is boiled in a bucket of water for half an hour . Then they add another bucket and water the bushes from a watering can.

Agrotechnical methods
The planting area is kept clean, weeds and plant debris are cleaned, the soil is loosened regularly, and it is disinfected before planting. In addition, crop rotation rules must be observed. Solanaceae are characterized by the same diseases, as well as pests. Therefore, neither before nor after pepper can you plant plants from this family.
Did you know? Red bell pepper has a large amount of lycopene, which prevents the formation of cancer cells.
Prevention
As a preventive measure, it is necessary to make a list of measures:
- use only healthy seeds and other planting material;
- grow resistant to Fusarium varieties;
- use only those seeds that have already been processed from fusarium at the production stage (the fact is indicated on the seed packaging);
- before planting, it is necessary to treat clean roots with fungicide in accordance with the instructions (as a rule, withstand pepper roots in a fungicide solution for 30 minutes);
- Before storing the fruits or sowing material for next year, the room must also be treated;
- observe crop rotation and irrigation;
- remove affected plants along with a lump of earth;
- burn diseased plants;
- wash equipment and garden tools that could come into contact with infected plants and disinfect it with technical alcohol;
- wash shoes on which, along with contaminated soil, there may be a source of fusarium;
- handle used pots and containers with bleach;
- disinfect soil with fungicides, soil for seedlings can be steamed;
- properly use fertilizers and nutritious fertilizing to increase plant immunity;
- mulch the planting with black or silver plastic wrap. This prevents the development of a pathogenic fungus.

Resistant varieties
Fortunately, breeders have created many varieties that are resistant to disease. The list below contains varieties with high resistance to fusarium wilt.
| Grade | Characteristic |
| Darina |
|
| Dobrynya |
|
| Beglitsky |
|
| Gift of Moldova |
|
| Everest |
|
| Bulgarian |
|
| Jeanne |
|









