Adromiscus: a description of the species, the cultivation and care at home
The succulent plant Adromiscus belongs to the family Crassulaceae and includes more than 70 species. Found in the wild in Africa. In our latitudes it is bred as a house plant, growing in pots. Adromiscus is undemanding to environmental conditions and unpretentious in care.
Types of hadromiscus and their description
Adromiscus is a stunted shrub or perennial herb with a stem creeping on the ground. The stems are covered with red-brown aerial roots, due to which the plant receives nutrition from the air. The leaves are succulent, thickened, rounded or triangular. Painted motley.

Did you know? Living adromiscus are used to create original jewelry. Properly caring for such a natural work of art, it can be used for 3-4 months. Most popular at home breeding:
- comb;
- spotted;
- schuldianus;
- Cooper;
- Pelnitsa.
Comb
The plant is a shrub with a height of 15 cm. On the stems there are even aerial roots of a reddish hue directed upwards. The shoots of a young plant are erect. As they grow older, they lie on the ground, transform into dangling or creeping. The leaf part is collected in several outlets. Leaves are slightly pubescent, ovally convex with wavy edges. The plates are painted in dark green color, their width is 5 cm, width - 1 cm. The flowers are light green, with a pink edging, appear in the warm season.

Spotted
A weakly branched small-sized succulent - spotted adromiscus - reaches a height of 10 cm. Dark green leafy plates are covered with red spots. They differ in a rounded shape. Their length is 5 cm, width - 3 cm. The flowers are red-brown, collected in a spikelet.

Schuldianus
The plant is a bush with shoots that end with ovoid leaf plates. The leaves are covered with a thin green film. A pink-red stripe runs along the pointed tip.

Cooper
Adromiscus Cooper is a compact bush with branching shoots. Leaf blades of oval shape, green, dotted with red-brown spots. The length of the leaves is 5 cm. Spike inflorescences are formed on a long flower garden during the warm period. They are painted red-green, along the edge are white or purple.

Pelnitsa
The height of the plant does not exceed 10 cm. The shoots branch. At the base are dense, convex, expand to the apex and transform into a plane with a wavy edge. The surface of the leaf plates is covered with barely noticeable white hairs. In the warm season, the plant throws a flower garden 40 cm long, on which inconspicuous flowers of white or pinkish color are located.

Breeding methods
There are 2 methods for the propagation of adromiscus:
- division of the bush;
- sheet.
Important! The procedure for separating the cuttings is carried out with a clean knife, disinfected in a 1% solution of potassium permanganate. Separate the selected stalk with a knife and dry the roots. To reduce the time, instead of drying, you can treat the roots with wood ash. In pre-prepared universal soil for cacti, make indentations and place cuttings in them. Around the shoots, you need to compact the soil well and cover the pot with a plastic bag.
As soon as you notice new buds on the shoots, you can remove the package. Do this gradually so that the plants become accustomed to a change in humidity. On the first day, leave the plant without a bag for 1 hour. Throughout the week, increase the time interval without a package by 1–1.5 hours. On day 8, remove the polyethylene completely.

After some time, "kids" will begin to appear on the sheet. They can be left this way or separated and planted in different pots. Separation of "children" should be carried out so that each has at least 1 root. Watering throughout the entire period of active vegetation is carried out as the soil coma dries up. In a year, the “children” will become fully-formed plants.
Care and necessary conditions for growing
Choosing adromiscus in the store, pay attention to its basal part. It should be dense, without traces of mechanical damage and rot. The leaves of a healthy plant are shiny, have a dense structure. Important! Planting of adromiscus is best done in the spring, because in winter the plant is at a dormant stage and it is undesirable to touch it. Immediately after planting, the plant needs to adapt to new conditions. Put it for 3 days in a dark place and do not water it. When the plant adapts, select a place for it on the south, east or southwest windowsill, where direct sunlight. For adromiscus, a small pot is suitable, at the bottom of which you must place a drainage. For these purposes, you can use sea pebbles or expanded clay.

Soil and fertilizer
For adromiscus, the soil of a loose structure is suitable. You can use the cactus soil mix you bought at the store. You need to add 1 part of coarse sand to it.
If desired, you can mix the soil yourself. This will require:
- 3 parts of coarse sand;
- 2 parts of garden soil;
- 2 parts of deciduous humus;
- 1 part of wood ash;
- chopped eggshell.
Video: Soil for succulents
Optimum temperature and humidity
In summer, the air temperature in a room with a succulent should be maintained within + 25-30 ° С. With an increase in the limit value, it is necessary to ensure free access of fresh air to the room. Watering is carried out as the earthen coma dries up, about once every 2 weeks. There is no need to regulate the humidity in the room. Succulents in this regard are not picky and well tolerate dry air.
In winter, it is necessary to provide the plant with peace and reduce the temperature to + 10-15 ° C. The lowest temperature that succulents can tolerate is +5 ° C. During the rest period, watering is completely excluded.
Light mode
Adromiscus grows well in direct sunlight. For its cultivation, poorly lit and dark rooms and window sills on the north side are not suitable. Plants will suffer from a lack of light, especially in winter. This situation can be corrected by additional illumination with fluorescent lamps.

Pruning and transplanting
Plant transplantation is carried out every 2-3 years. Over the entire period of active vegetation, adromiscus forms 2-3 new leaves, so it does not need frequent transplantation. The procedure is carried out by the transshipment method. The pot is selected 1 finger larger than the previous one. 2 days before and 2 days after transplantation, the succulent is not watered and placed in a dark place. 48 hours after transplantation, the plant is again exposed to its former habitat and carefully watered.
Pruning is carried out as necessary in the presence of damaged and dry leaves, in the spring - after leaving the dormant state in order to slightly thin out the crown. Cropped leaves can be used to breed new plants.
Important! As they grow older, the lower leaves of adromiscus become thinner, lose their color and die. During this period, you just need to remove dead leaves to enable the plant to fully develop new leaf plates.
Features after flowering
After flowering, you need to cut off the peduncle at the root. If this is not done, root rot may develop. Otherwise, after flowering, standard care.

Growing difficulties
If the rules of agricultural technology are not followed, the following problems may appear:
- Basal rot - manifested when water enters a leafy outlet. An urgent transplant with preliminary pruning of the affected parts of the plant and drying will help to solve the problem.
- Yellowing and wilting of leaves - appears with waterlogging of the soil and sunburn. The situation with increased humidity is corrected by transplantation. In case of a burn, the plant may, over time, restore the color of the leaves on its own or begin to discard them. The burn does not require specific treatment, just remove the adromiscus in another place and provide sufficient watering.
- Cracking of leaf plates - appears with insufficient watering. They correct the situation by regulating agrotechnical conditions, teaching watering and conducting periodic spraying.
- Deformation of leaves and shoots - signals a lack of lighting. Moving a flower pot to a lighter room or organizing additional lighting will help solve the problem.
- aphids - small or small green or black bugs settle on leaflets and feed on their juice, which leads to drying out;

- mealybug - in the axils of deciduous rosettes a sugar-like cobweb-like substance appears that interferes with normal photosynthesis;
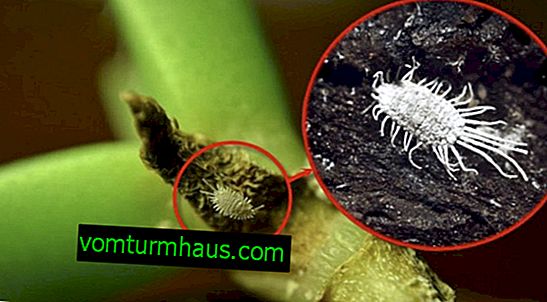
- spider mite - the leaves are covered with a white coating, they lose their density and turn yellow.

- against aphids - 1 ampoule / 0.6 l of water;
- from a spider mite and a worm - 1 ampoule / 2.5 l of water.
Did you know? After watering, succulents store liquid in an aquiferous parenchyma. This is a fabric that consists of large vacuoles filled with juice. In adromiscus, this tissue is in deciduous plates. In the wild, the plant absorbs so much moisture that its weight increases immediately by 2-3 times. Adromiscus is an unpretentious home plant that belongs to the cactus. It tolerates heat and dry air. It is steady against diseases at observance of elementary agrotechnical rules.






